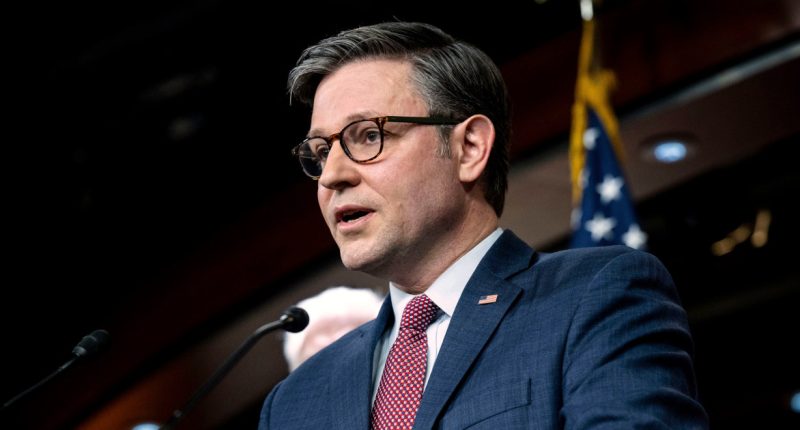
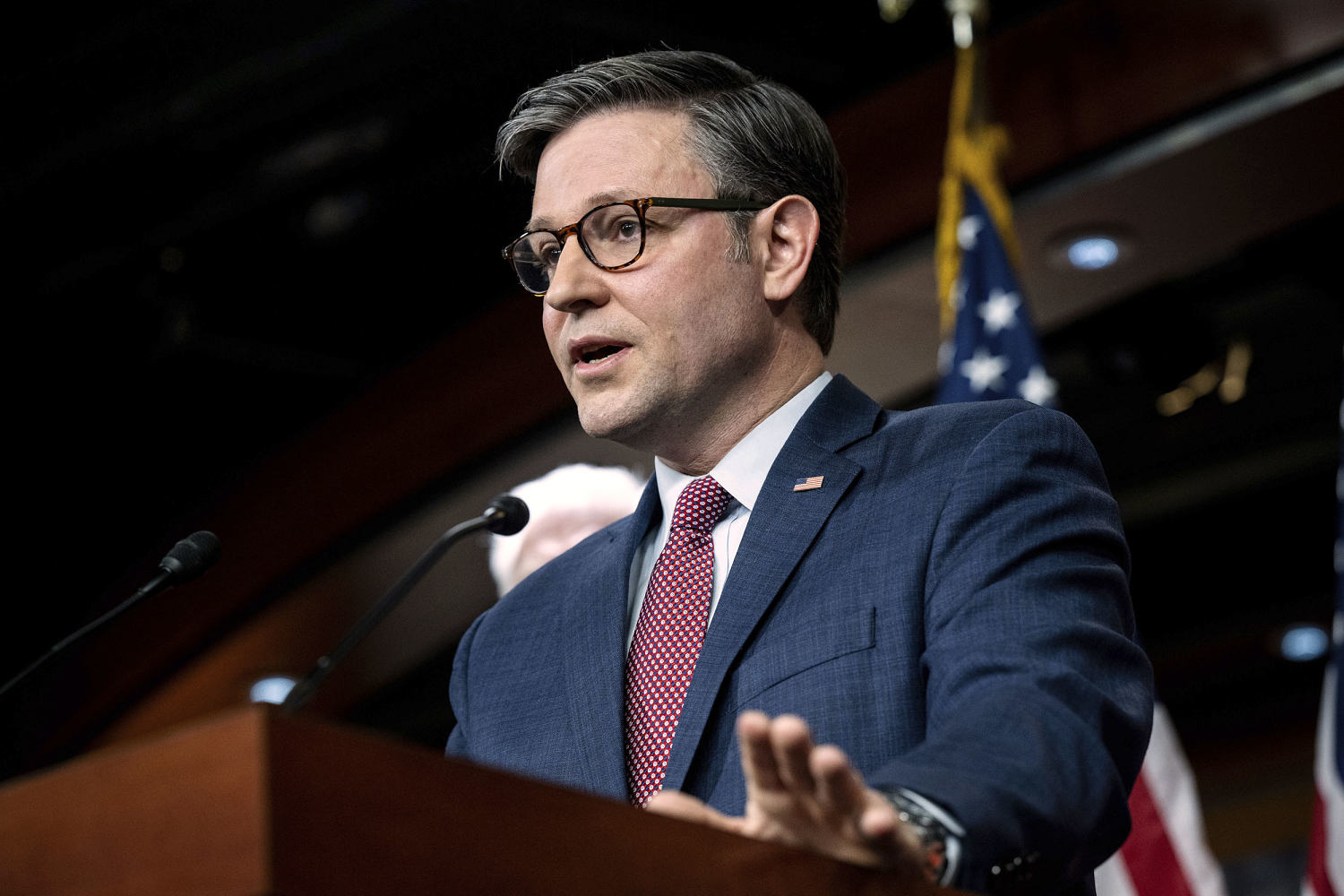
GOP Policy Committee Chairman Gary Palmer, R-Ala., who briefly ran for speaker before dropping out, said he got to know Johnson before they were elected to Congress, when both were working for conservative organizations. (Johnson worked at the evangelical legal group, the Alliance Defending Freedom, where he wrote briefs and op-eds opposing LGBTQ rights). Both men joined the House Freedom Caucus but soon left the group of far-right rabble-rousers as they eyed leadership posts.
“He’s very level-headed, not one to get emotional. He’s a great communicator and he’s focused,” Palmer said Friday.
Johnson’s elevation from relative unknown to speaker is unusual. Paul Ryan had been the GOP’s vice presidential nominee and chairman of two House committees, Budget and Ways and Means, before his elevation to speaker in 2015. And McCarthy had worked his way through almost every leadership post — chief deputy whip, majority whip, majority leader, minority leader — before winning the coveted gavel in January.
The job was going to be difficult for whoever stepped into the role, but it’s an especially steep learning curve for Johnson given the stakes: Government funding is set to run out by Nov. 17, and two key U.S. allies, Ukraine and Israel, are asking for military aid as they wage war against Russia and Hamas. But Johnson’s allies push back at any suggestion that his inexperience and lack of relationships across the capital city put him at a disadvantage at this pivotal moment.
“He stands in the catbird seat: They don’t know him, but he knows them, so he’s got a head start,” Rep. Tim Walberg, R-Mich., said in an interview. “He can say, ‘I know how Chuck Schumer works, I know his positions. I’m a little bit of a mystery to him.’”
Johnson also huddled with Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries, D-N.Y., this week, and met for 45 minutes with McConnell, according to two sources, before addressing Senate Republicans at a closed-door lunch on Wednesday.
Before becoming speaker, Johnson had joined fellow House conservatives in voting no on Ukraine aid packages. But in his meeting with senators, Johnson assured the room that he is in favor of sending aid to Ukraine, and favors a path that combines Ukraine funding with border security policies, senators said.
Johnson told senators that border security and Ukraine aid are “inextricably intertwined,” according to Sen. John Cornyn, R-Texas, who himself is a part of the Senate GOP group crafting border policies that could potentially be included in such a package.
The speaker told senators he needs to adjust his opposition to Ukraine aid now that he occupies the top job and has to reflect the views of his broader conference, said Sen. Ron Johnson, R-Wis., who is not related. The speaker also told senators he prefers a short-term stopgap funding measure, known as a continuing resolution or CR, that would keep the government funded through Jan. 15.
“He’s speaker of the House. He’s got a very slim majority,” said Sen. Johnson, who introduced the new speaker to the room.
Johnson may have secured unanimous GOP support for speaker, but his early days haven’t been free from criticism. Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene, R-Ga., was one of two Republicans who voted no on Johnson’s Israel aid package. She doesn’t fault him for putting that aid on the floor, but she expressed frustration with Johnson for failing to pass her resolution censuring Rep. Rashida Tlaib, D-Mich., for her criticism and protests of Israel.
“No one whipped that, no one worked it, no one communicated with me people’s concerns about language in the bill. And I’m very angry about that,” Greene said Friday.
Jeffries, the Democratic leader, has criticized Johnson’s approach of tying $14.3 billion in Israel aid to cuts to the IRS, calling it a “partisan political stunt.” But he has not personally attacked Johnson, appearing to give the new speaker some leeway. Rank-and-file Democrats, however, were furious at Johnson’s tactic, saying many of them would have rallied behind a clean Israel aid package that didn’t cut domestic programs. Instead of a big, bipartisan vote on aid, only 12 Democrats backed Johnson’s aid bill.
“His very first act of Congress was to put a bipartisan resolution that got over 400 votes condemning Hamas, supporting Israel, on the board. We know he knows how to work in a bipartisan fashion,” Rep. Hillary Scholten, D-Mich., said in an interview.
“I’m deeply disappointed to see the actions that he’s taken this week that completely run counter to that narrative. … Speaker Johnson is choosing to prioritize a MAGA wishlist over the interest of our democratic allies around the country,” she said.
Source: | This article originally belongs to Nbcnews.com