THE lack of gravity in space could be harming astronaut bones more than previously thought.
Spending a long time in the microgravity of space could even affect astronaut bones for a year after they return to Earth, according to a new study.
University of Calgary biomedical engineer Steven Boyd led the new international research.
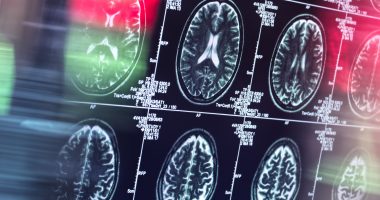
His team scanned the bones of 17 astronauts.
This included 14 males and three females.
Their bones were tested before and after time in space.


They were scanned at six months and one year after the return.
It wasn’t unusual to see bone loss in the astronauts as we already know that microgravity can have this effect.
What was unusual was how long the astronauts took to return to their original bone strength.
Fortunately, the scientists think they have a solution to the problem.
Most read in Tech
That solution is deadlifts.
Boyd explained: “Different kinds of exercise have different effects.
“So although bone is influenced by load, impact loading is better than continuous loading.”
The researchers used advanced scanning technology to study the bones and think it helped them draw new conclusions than older research.
Boyd added: “It’s a whole bunch of struts and rods that are all interconnected to give bones strength.
“With this technology, we can see those struts and rods, and we can then measure how they are affected by spaceflight and what happens when you return to Earth.”
Unfortunately, some of that internal structure in the bone doesn’t comeback after a return from space.
Although astronauts can work to recover their bone strength, Boyd says “the actual underlying structure might be permanently altered.”
The new research could help space agencies come up with effective space training regimes so astronauts are protected.
This will be especially useful for long space missions.
It’s expected that a Mars mission could take two to three years and that’s a lot of time to be in space.
The study has been published in Scientific Reports.
What happens to bones in space?
Scientists have known for decades that space weakens human bones.


The Nasa website explains: “Nasa has learned that without Earth’s gravity affecting the human body, weight-bearing bones lose on average 1% to 1.5% of mineral density per month during spaceflight.
“After returning to Earth, bone loss might not be completely corrected by rehabilitation; however, their risk for fracture is not higher.”