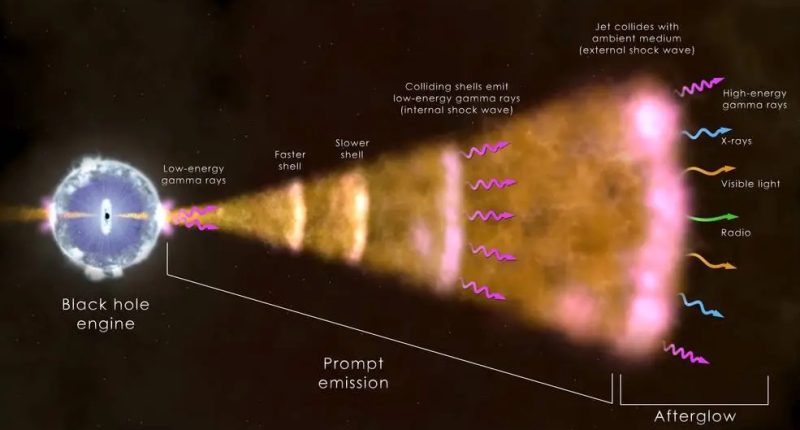
NEW analysis of the most powerful space explosion ever seen has revealed a fascinating discovery.
The large bang that resulted in the birth of a black hole can be seen in a Nasa timelapse.
It was spotted in October 2022 during a study that was already monitoring the skies for explosions, according to Live Science.
Nasa’s James Webb Space Telescope caught the explosion in action and allowed researchers to study it.
The event was the biggest burst of gamma radiation ever recorded.
That’s how it got the nickname BOAT, which stands for Brightest of All Time.
Researchers soon discovered the event was a violent supernova that resulted in the birth of a black hole.
It’s still known as the biggest gamma-ray burst (GRB) but new research suggests it was not any brighter than previous supernovae.
Researchers also hoped they would find evidence of the supernova producing heavy elements like platinum and gold.
No evidence of this was found and the origin of those elements is still a mystery.
Most read in Science
The new study has been published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
“When we confirmed that the GRB was generated by the collapse of a massive star, that gave us the opportunity to test a hypothesis for how some of the heaviest elements in the universe are formed,” said Northwestern’s Peter Blanchard, who led the study.
“We did not see signatures of these heavy elements, suggesting that extremely energetic GRBs like the B.O.A.T. do not produce these elements.
“That doesn’t mean that all GRBs do not produce them, but it’s a key piece of information as we continue to understand where these heavy elements come from.
“Future observations with JWST will determine if the B.O.A.T.’s ‘normal’ cousins produce these elements.”
The scientist added that the event also wasn’t found to be unusually bright.
“It’s not any brighter than previous supernovae,” Blanchard said. “It looks fairly normal in the context of other supernovae associated with less energetic GRBs.
“You might expect that the same collapsing star producing a very energetic and bright GRB would also produce a very energetic and bright supernova.
“But it turns out that’s not the case. We have this extremely luminous GRB, but a normal supernova.”
What is a black hole? The key facts
Here’s what you need to know…
- A black hole is a region of space where absolutely nothing can escape
- That’s because they have extremely strong gravitational effects, which means once something goes into a black hole, it can’t come back out
- They get their name because even light can’t escape once it’s been sucked in – which is why a black hole is completely dark
What is an event horizon?
- There has to be a point at which you’re so close to a black hole you can’t escape
- Otherwise literally everything in the universe would have been sucked into one
- The point at which you can no longer escape from a black hole’s gravitational pull is called the event horizon
- The event horizon varies between different black holes, depending on their mass and size
What is a singularity?
- The gravitational singularity is the very centre of a black hole
- It’s a one-dimensional point that contains an incredibly large mass in an infinitely small space
- At the singularity, space-time curves infinitely and the gravitational pull is infinitely strong
- Conventional laws of physics stop applying at this point
How are black holes created?
- Most black holes are made when a supergiant star dies
- This happens when stars run out of fuel – like hydrogen – to burn, causing the star to collapse
- When this happens, gravity pulls the centre of the star inwards quickly, and collapses into a tiny ball
- It expands and contracts until one final collapse, causing part of the star to collapse inward thanks to gravity, and the rest of the star to explode outwards
- The remaining central ball is extremely dense, and if it’s especially dense, you get a black hole