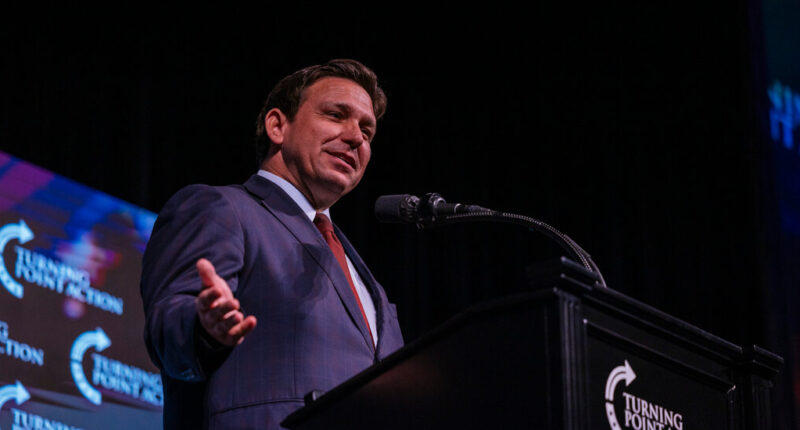
Over the past two months, Gov. Ron DeSantis of Florida has repeatedly declared victory in his yearlong effort to restrict the autonomy of Disney World, the state’s largest employer. “There’s a new sheriff in town,” he said numerous times, including at a news conference last month on Disney property, hours before appointing a new, handpicked oversight board.
Nobody seemed to have paid attention, however, to an important detail: Disney had been simultaneously maneuvering to restrict the governor’s effort. In early February — at a public meeting held by the previous, Disney-controlled oversight board — the company pushed through a development agreement that would limit the new board’s power for decades to come.
And now, the governor’s appointees, having belatedly discovered the action, are none too pleased. “It completely circumvents the authority of the board to govern,” Brian Aungst Jr., a member of the new council, said on Wednesday at the group’s second meeting. “We’re going to have to deal with it and correct it.”
Mr. DeSantis has not weighed in personally, but a spokeswoman, Taryn Fenske, said in a statement that the new board had retained multiple legal firms “to conduct audits and investigate Disney’s past behavior.” Ms. Fenske added that the administration expected that the “last-ditch effort” by Disney would be found “void as a matter of law.”
Disney disagreed.
“All agreements signed between Disney and the district were appropriate and were discussed and approved in open, noticed public forums in compliance with Florida’s Government-in-the-Sunshine law,” Disney said in a statement.
More on the Walt Disney Company
The upshot: The fight between Disney and Florida Republicans seems far from over.
The sparring started a year ago, when Mr. DeSantis asked Florida lawmakers to terminate self-governing privileges that Disney World had held since 1967. The privileges, formally called a special tax district, effectively allowing the company to self-govern its 25,000-acre theme park complex as a de facto county, controlling fire protection, policing, road maintenance — and, crucially, development planning.
The move was widely seen as retaliation for Disney’s opposition to a new state education law that the bill’s opponents call “Don’t Say Gay.” Among many things, the law prohibits discussion about sexual orientation and gender identity through the third grade in Florida classrooms and limits it for older students. Disney paused political donations in Florida as a result of the law.
The Legislature went along with Mr. DeSantis until it realized there was a problem. The abolishment of the district — set for June 1, 2023 — would require taxpayers in Orange and Osceola Counties to pick up the tab for some Disney World services. Under the old setup, Disney paid for fire protection, policing and road maintenance. The district also carried roughly $1 billion in debt. If the district had been abolished, that debt would have been transferred to the counties.
So the Legislature tried again, taking up a new Disney World measure in a special session that started on Feb. 6 and passing it on Feb. 10. This time, Disney was allowed to keep the special tax district — which never went away — and almost all its perks, including the ability to issue tax-exempt bonds. But Disney was no longer able to appoint the five members of the tax district’s board. Florida’s governor would now do that.
In the middle of that week, on Feb. 8, the tax district’s board — the Disney-controlled one — passed restrictive covenants and a development agreement giving the company vast control over future construction in the district; the new board doesn’t have any say.
Furthermore, the agreement is effective for perpetuity, according to the agreement, which uses contractual language known as a “royal lives” clause: “Shall continue in effect until twenty one (21) years after the death of the last survivor of the descendants of King Charles III, King of England living as of the date of this declaration.” (The royal language quickly spawned numerous internet memes, striking people as odd in a matter involving a theme park that is home to Cinderella’s Castle.)
The agreement also prohibits the tax district, now called the Central Florida Tourism Oversight District, from using Disney’s name, Mickey Mouse and other characters without the company’s approval. Disney can sue for damages for violations.
“The board loses, for practical purposes, the majority of its ability to do anything beyond maintain the roads and maintain basic infrastructure,” Ron Peri, a member of the new board, told The Orlando Sentinel.
Source: | This article originally belongs to Nytimes.com